Refereed paper by Kadri, F.L. and Duncan, I.J.,
published in Behavioural Processes v.33 (1995) pp. 273-288
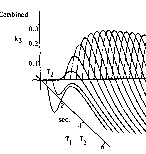
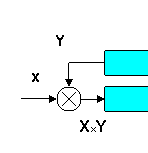
To propose a mathematically rigorous dynamic nonlinear model of motivation combining priming and homeostatic mechanisms.
Minimum recommended background:
1- Working knowledge of Laplace Transforms
2- Basic knowledge of Multidimensional Laplace Transform (MLT) techniques, see for example chapters 1 to 7 in book: Schetzen, M, "The Volterra and Wiener Theories of Nonlinear Systems", Wiley, New York 1980. Continue reading "A New Nonlinear Model of Mechanism of Motivation" »