Summary
The average funniness score of individuals is a by-product of scaling raw scores, the correlation between average scores and Big Five traits found significant correlation with Extroversion and Neuroticism. Correlation with raw scores found similar results in earlier studies, suggesting that the average funniness score is a major contributor to linking humour with two traits.
Then, scaled scores were aggregated in keyed groups of 5 high/low loadings and correlated with Big Five traits, correlation profiles showed a signature plateau pattern predominant across gender and age trends, most notedly, near zero dip in correlation with the same two traits. The existence of the signature pattern suggests the possibility of predicting Big Five traits in two steps. Computing the relative entropy (Kullback-Leibler diversion) provide assessment of the accuracy of prediction.
The age profiles showed jagged but generally declining correlation between Big Five and funniness, suggesting declining dependence of personality on age at adulthood.
Conclusion: Assessed relative entropy of predicting personality traits from funniness scores. Scores need to be scaled in order to improve prediction.
Kadri, F.L.(2022). The Entropy of Predicting Personality from Funniness Scores. International Journal of Research -GRANTHAALAYAH, 10(7), 80–90. DOI: 10.29121/granthaalayah.v10.i7.2022.4666
https://www.granthaalayahpublication.org/journals/granthaalayah/article/view/4666/4776
Monday, August 8. 2022
The Entropy of Humour Predictions of Personality
Reinventing personality from a Volterra nonlinear model of motivation
Summary
A mathematical model of animal behaviour was suggested in 1995, it combined priming and homeostatic mechanisms into one dynamic nonlinear systems.
Projecting the model over human behaviour led to a cybernetic theory of aging, where the brain acts as an information channel with diminishing bandwidth: Anecdotal age related changes in human perception could be explained by the age related reduction in bandwidth.
Analyzing funniness raw scores is a convenient way of testing the predicted changes. 100 Humorous sentences were classified in four age trends and tested for internal consistency. Comparing with 100 Big Five personality scores, funniness scores showed higher internal consistency. Significant correlation coefficients were found between humour and two traits, confirming earlier research.
Conclusion: Humour/funniness raw scores could be more reliable than personality self-assessment in identifying individual personality traits.
Citation
Kadri, F. (2022). Reinventing personality from a Volterra nonlinear model of motivation. Acta Europeana Systemica , 11(1), 41-58. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14428/aes.v11i1.63013
A mathematical model of animal behaviour was suggested in 1995, it combined priming and homeostatic mechanisms into one dynamic nonlinear systems.
Projecting the model over human behaviour led to a cybernetic theory of aging, where the brain acts as an information channel with diminishing bandwidth: Anecdotal age related changes in human perception could be explained by the age related reduction in bandwidth.
Analyzing funniness raw scores is a convenient way of testing the predicted changes. 100 Humorous sentences were classified in four age trends and tested for internal consistency. Comparing with 100 Big Five personality scores, funniness scores showed higher internal consistency. Significant correlation coefficients were found between humour and two traits, confirming earlier research.
Conclusion: Humour/funniness raw scores could be more reliable than personality self-assessment in identifying individual personality traits.
Citation
Kadri, F. (2022). Reinventing personality from a Volterra nonlinear model of motivation. Acta Europeana Systemica , 11(1), 41-58. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14428/aes.v11i1.63013
Thursday, July 27. 2017
Download The Design and Validation of an Artificial Personality
Here is the text version of article published in Kybernetes:
DesignValidationArtificialPsychology.pdf
DesignValidationArtificialPsychology.pdf
Tuesday, June 24. 2014
The Cybernetics of Humor

Presented to the American Society for Cybernetics conference, Washington DC, August 2014
The Cybernetics of Humor; The Application of Signature Analysis to Humor
Second edition of eBook available on-line from Amazon.
Continue reading "The Cybernetics of Humor" »
Saturday, December 8. 2012
A Primer on the Interpretation of Humor

Humor is probably a uniquely human characteristic, here humor is defined as A sudden falsification of perceived threat. The falsification presumes the perception of a lie, humans can recognize a lie, animals maybe not.
Continue reading "A Primer on the Interpretation of Humor" »
Tuesday, October 4. 2011
The Design and Validation of an Artificial Personality

The purpose of the paper is to expose the usefulness and scientific roots of the Artificial Psychology patent and support its commercial viability by statistical evidence.
Article published by:
Kybernetes, Vol. 40 No. 7/8, 2011
Full text is obtainable on-line.
Continue reading "The Design and Validation of an Artificial..." »
Friday, August 5. 2011
Comparing Regulators: The Homeostat vs. Multiplier Feedback
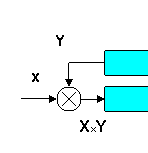
To be presented at the American Society for Cybernetics conference, Richmond IN, August 2011
To compare the regulation mechanisms of negative feedback with multiplier feedback. Continue reading "Comparing Regulators: The Homeostat vs...." »
Friday, July 8. 2011
What Cybernetics Got to do with Humor Research?

Presented at the annual ISHS meeting at Boston in July 2011.
To introduce second order cybernetics concepts to humor research. Continue reading "What Cybernetics Got to do with Humor Research?" »
Tuesday, January 5. 2010
Artificial Psychology Dialog Player with Aging Simulation

US Patent #7644060 issued on Jan. 5, 2010
An artificial psychology dialog player is a software program that picks a sentence line from a repertoire according to probabilistic rules and artificial personality states. The model of personality has four motivational dimensions, one of which (the emotions) is always paired with one of the remaining three (feeding, sociosexual and parenting motivations); each pair is identified with a stage of human age. Continue reading "Artificial Psychology Dialog Player with Aging..." »
Thursday, February 19. 2009
New Survey Confirms Link between Humor Preference and Age-Personality

Internet TechNote February 18, 2009
The purpose is to confirm the humor/age link and to seek humor/personality link in order to support a patent application.
A humor appreciation internet survey with 40 humor lines and 20/50 Big 5 (B5) personality items ran for the span of 2008. The humor/age link of the previous survey was confirmed and evidence was found that humor scores are correlated mainly with the emotional stability factor of the B5, while cognitive scores (differential) are linked with the remaining four cognitive factors. The correlation coefficients were too small to show specifics of factor links it was thought hat this is due to the small number of participants.
Continue reading "New Survey Confirms Link between Humor..." »
Sunday, December 9. 2007
Humor preference changes with age

Internet TechNote December 8, 2007
The purpose is to explore the statistical basis for a possible patent application based on the 4D model.
Two humor appreciation internet surveys ran in 2007, the humor lines were interpreted according to the 4D model and the scores analyzed against age and gender variation. The analysis supported age prediction with statistical significance but no significant gender difference. The statistics in effect provided initial validation. Continue reading "Humor preference changes with age" »
Sunday, March 26. 2006
Personality between Cognition and Motivation
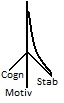
Internet TechNote March 26, 2006
To describe a hypothesis of personality structure where the dimensions derived by factor analysis can be interpreted in dual cognitive and motivational context.
Comparing the descriptions of the four drives (4D) with the dimensions of some well known personality models reveals a more complex structure than the simple two dimensional tables shows. The novelty is to interpret in two contexts: cognition and motivation, some dimensions appear to be referenced in a cognitive manner, others in motivational manner and the remaining seem mixed or rotated between the two. Continue reading "Personality between Cognition and Motivation" »
Thursday, March 16. 2006
Aging between Cognition and Motivation

Internet TechNote March 16, 2006
To explain an intuitive rationale behind linking humor type preference to post adulthood age.
Humans are considered mature and accountable usually at age 18 yet their behavior keeps developing afterwards. Post adulthood age related behavioral development cannot be attributed to cognition otherwise it would be a legal issue, e.g. a systematic factor in determining the guilt or innocence beyond adulthood. Behavioral development has to be attributed to motivation.
Continue reading "Aging between Cognition and Motivation" »
Artificial Intelligence between Cognition and Motivaton

Internet TechNote March 16, 2006
The purpose is to present arguments that support the duality of cognition and motivation
Cognition alone cannot mimic human behavior; not only because cognition is static but also because cognition requires motivation in order to define its context.
Continue reading "Artificial Intelligence between Cognition and..." »
(Page 1 of 2, totaling 24 entries)
next page »



